
Calculate trend correlations based on latent factor loadings for mvgam models
Source:R/lv_correlations.R
lv_correlations.RdThis function uses factor loadings from a fitted dynamic factor
mvgam model to calculate temporal correlations among series' trends.
Arguments
- object
listobject of classmvgamthat used latent factors, either withuse_lv = TRUEor by supplying atrend_map. Seemvgam()for details and for an example.
Value
A list object containing the mean posterior correlations and
the full array of posterior correlations.
Details
Although this function will still work, it is now recommended to use
residual_cor() to obtain residual correlation information in a more
user-friendly format that allows for a deeper investigation of relationships
among the time series.
Examples
# \dontrun{
#--------------------------------------------------
# Fit a model that uses two AR(1) dynamic factors to model
# the temporal dynamics of the four rodent species in the portal_data
#--------------------------------------------------
mod <- mvgam(
captures ~ series,
trend_model = AR(),
use_lv = TRUE,
n_lv = 2,
data = portal_data,
chains = 2,
silent = 2
)
#> Warning in '/tmp/Rtmpz9mhjG/model_fd0fdfeaee023a8e623b5071c6b9ec02.stan', line 20, column 31 to column 48:
#> Found int division:
#> n_lv * (n_lv - 1) / 2
#> Values will be rounded towards zero. If rounding is not desired you can
#> write the division as
#> n_lv * (n_lv - 1) / 2.0
#> If rounding is intended please use the integer division operator %/%.
#> Warning in '/tmp/Rtmpz9mhjG/model-21122f1fe7a.stan', line 20, column 33 to column 50:
#> Found int division:
#> n_lv * (n_lv - 1) / 2
#> Values will be rounded towards zero. If rounding is not desired you can
#> write the division as
#> n_lv * (n_lv - 1) / 2.0
#> If rounding is intended please use the integer division operator %/%.
# Plot the two dynamic factors
plot(mod, type = 'factors')
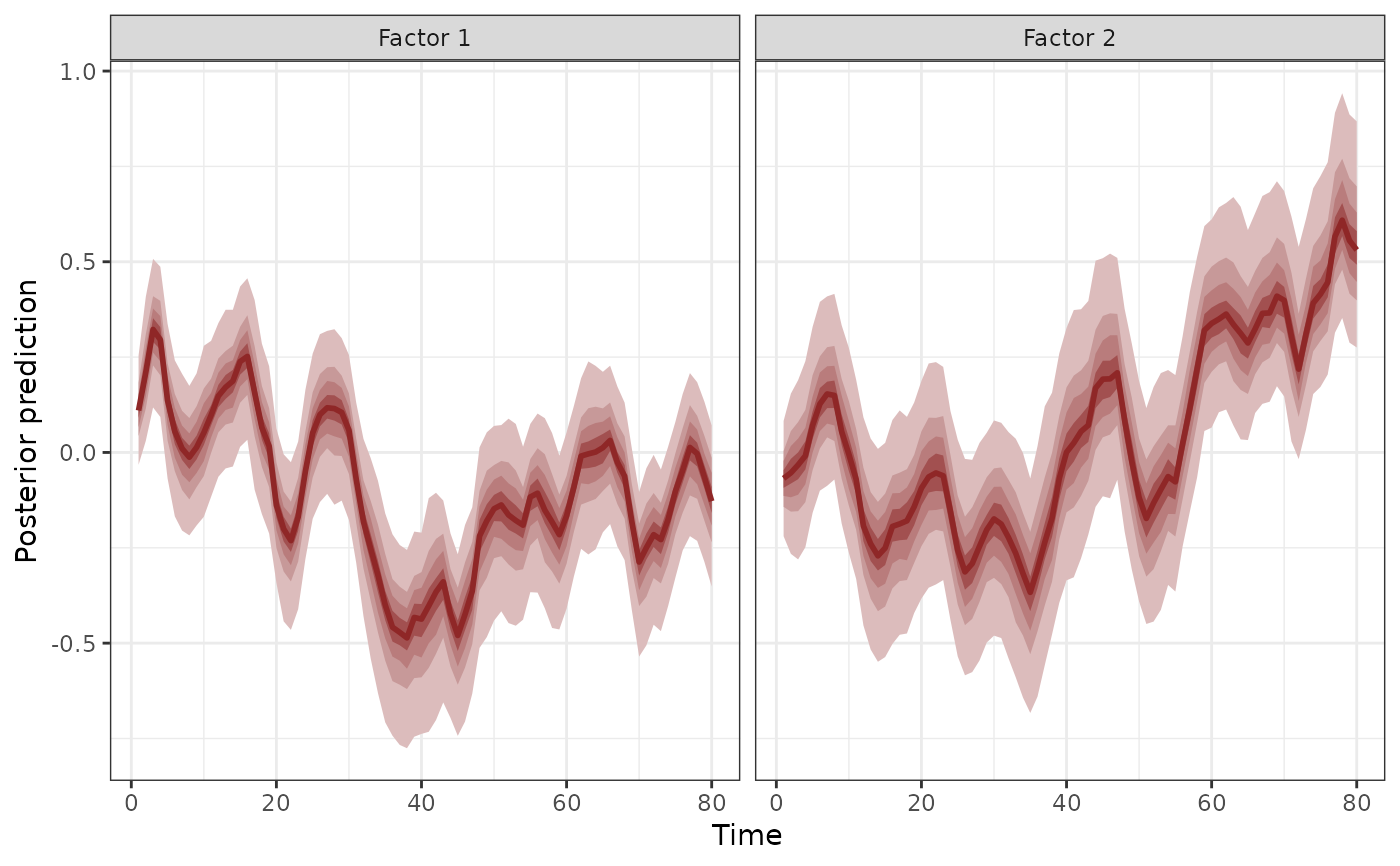 #> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> Factor Contribution
#> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 Factor 1 0.534
#> 2 Factor 2 0.466
# Calculate correlations among the series
lvcors <- lv_correlations(mod)
names(lvcors)
#> [1] "mean_correlations" "posterior_correlations"
lapply(lvcors, class)
#> $mean_correlations
#> [1] "matrix" "array"
#>
#> $posterior_correlations
#> [1] "list"
#>
# Recommended: use residual_cor() instead
lvcors <- residual_cor(mod)
names(lvcors)
#> [1] "cor" "cor_lower" "cor_upper" "sig_cor" "cov"
#> [6] "prec" "prec_lower" "prec_upper" "sig_prec" "trace"
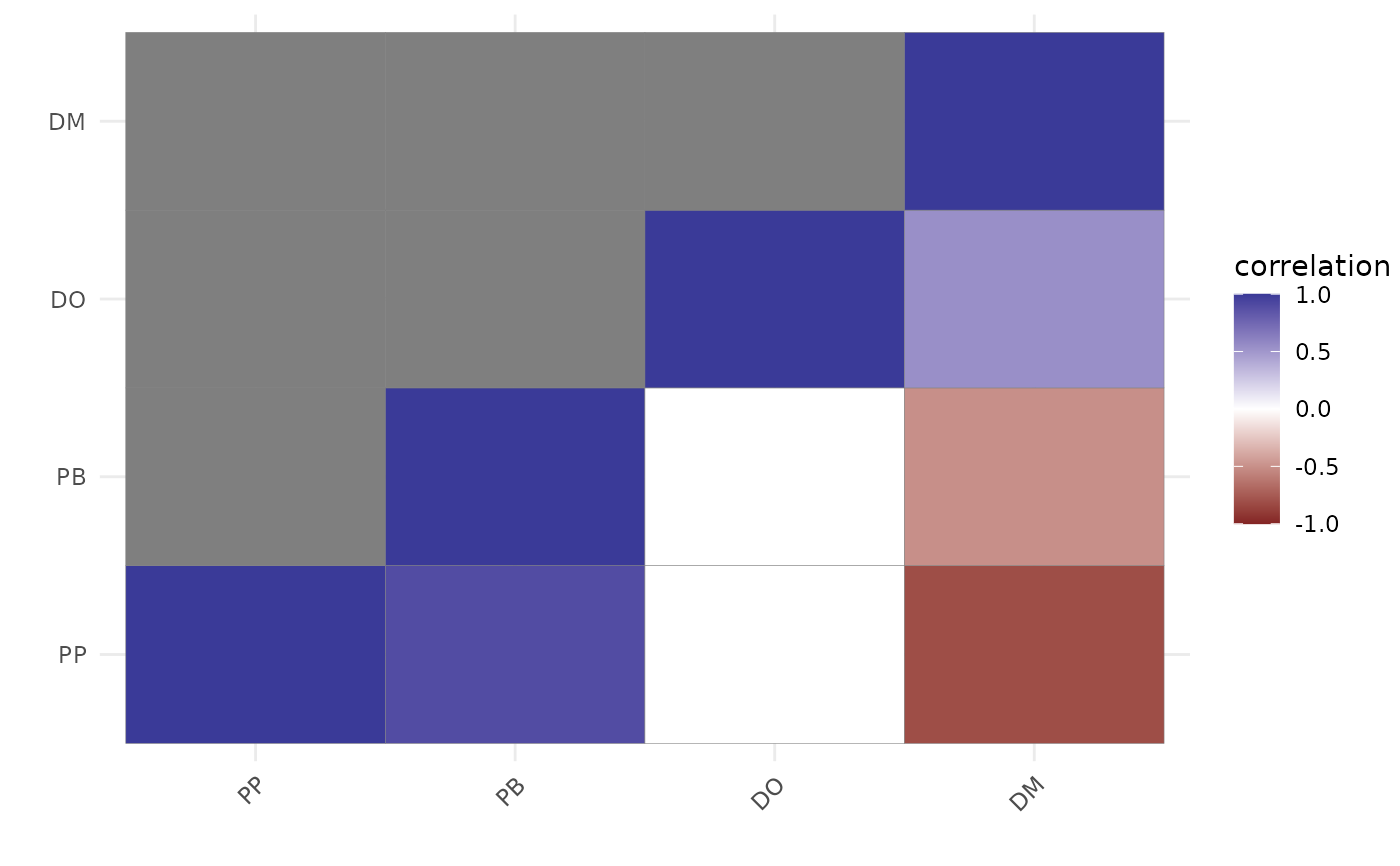
lvcors$cor
#> DM DO PB PP
#> DM 1.0000000 0.54925545 -0.4794042 -0.79837885
#> DO 0.5492555 1.00000000 0.4290647 0.01890233
#> PB -0.4794042 0.42906470 1.0000000 0.89413740
#> PP -0.7983788 0.01890233 0.8941374 1.00000000
# Plot credible correlations as a matrix
plot(lvcors, cluster = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> Factor Contribution
#> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 Factor 1 0.534
#> 2 Factor 2 0.466
# Calculate correlations among the series
lvcors <- lv_correlations(mod)
names(lvcors)
#> [1] "mean_correlations" "posterior_correlations"
lapply(lvcors, class)
#> $mean_correlations
#> [1] "matrix" "array"
#>
#> $posterior_correlations
#> [1] "list"
#>
# Recommended: use residual_cor() instead
lvcors <- residual_cor(mod)
names(lvcors)
#> [1] "cor" "cor_lower" "cor_upper" "sig_cor" "cov"
#> [6] "prec" "prec_lower" "prec_upper" "sig_prec" "trace"
lvcors$cor
#> DM DO PB PP
#> DM 1.0000000 0.54925545 -0.4794042 -0.79837885
#> DO 0.5492555 1.00000000 0.4290647 0.01890233
#> PB -0.4794042 0.42906470 1.0000000 0.89413740
#> PP -0.7983788 0.01890233 0.8941374 1.00000000
# Plot credible correlations as a matrix
plot(lvcors, cluster = TRUE)
 # Not needed for general use; cleans up connections for automated testing
closeAllConnections()
# }
# Not needed for general use; cleans up connections for automated testing
closeAllConnections()
# }